Written by
Carissa O'Connell
Nov. 28, 2022; Updated: Jan 2023
As times change, programs should also evolve to meet the current needs of the business. In order for the program to be setup so that it could operate according to the current needs of the users, the program would need to be designed to include the necesssary features. Understanding the different types of software methodologies could define the abilities of the program and how the program could transform a business.

By understanding each type of methodolgy, it helps to determine which methodology could work best for the team and project. Depending on the size of the team, the teams experience and expertise in the methodology, the deadline for the project, and the type of project being developed, certain methodologies would work best. To determine which type of methodolgy to utilize for the team and the project, you could refer to "How to choose a Software Methodology" for more information.
In this article, we will review 15 different types of software development methodologies
- Agile Development
- Lean Software Development
- Waterfall Methodology
- Extreme Methodology
- DevOps Development
- Prototyping Methodology
- Dynamic Systems Development
- Feature Driven Development
- Rational Unified Process
- Spiral Development Model
- Joint Application Development
- Kanban
- Scrum Development
- Rapid Application Development
- Continuous Development
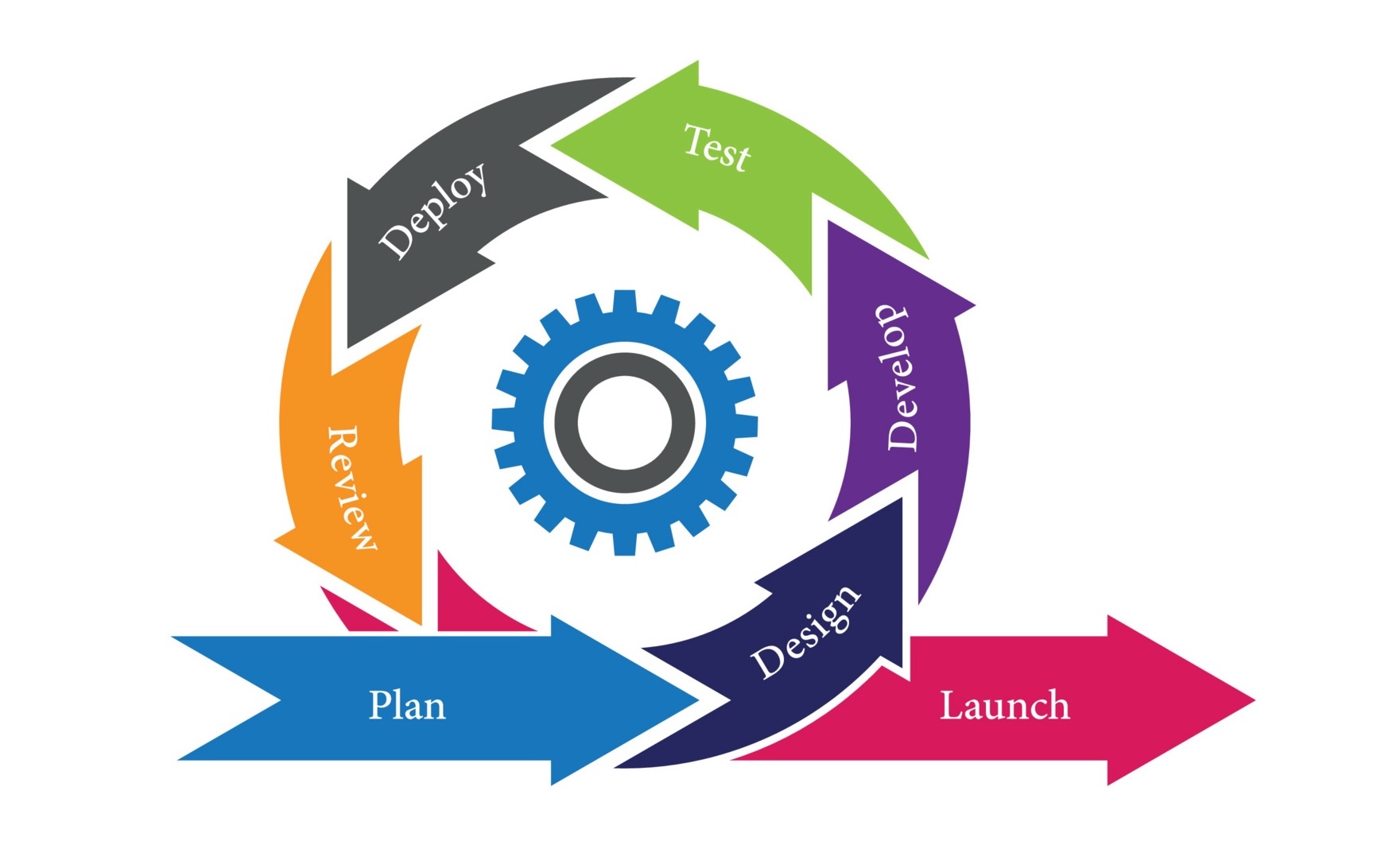
Agile methodology is a project management approach that prioritizes cross-functional collaboration and continuous improvement. It divides projects into smaller phases and guides teams through cycles of planning, execution, and evaluation.
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
Back to index of Methodologies

The lean software development methodology is one of the software design methods with a main focus on loss reduction. That is why the whole project is examined significantly beforehand to eliminate any wasted time or money. As value is the core component, feedback plays a crucial role itself, so that the actions are taken fast.
- Focus on continuous improvement and waste elimination
- Iterative and collaborative approach
- Development of Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
- Customer involvement and feedback
- Flexible and adaptive approach
- Prioritization of essential functions and minimization of waste
Lean Software Development (LSD) is an agile framework that is used to streamline & optimize the software development process. It may also be referred to as Minimum Viable Product (MVP) strategy as these ways of thinking are very much alike since both intend to speed up development by focusing on new deliverables.
- Eliminating the waste
- Fast Delivery
- Amplify Learning
- Builds Quality
- Respect Teamwork
- Delay the commitment
- Optimizing the whole system
Back to index of Methodologies
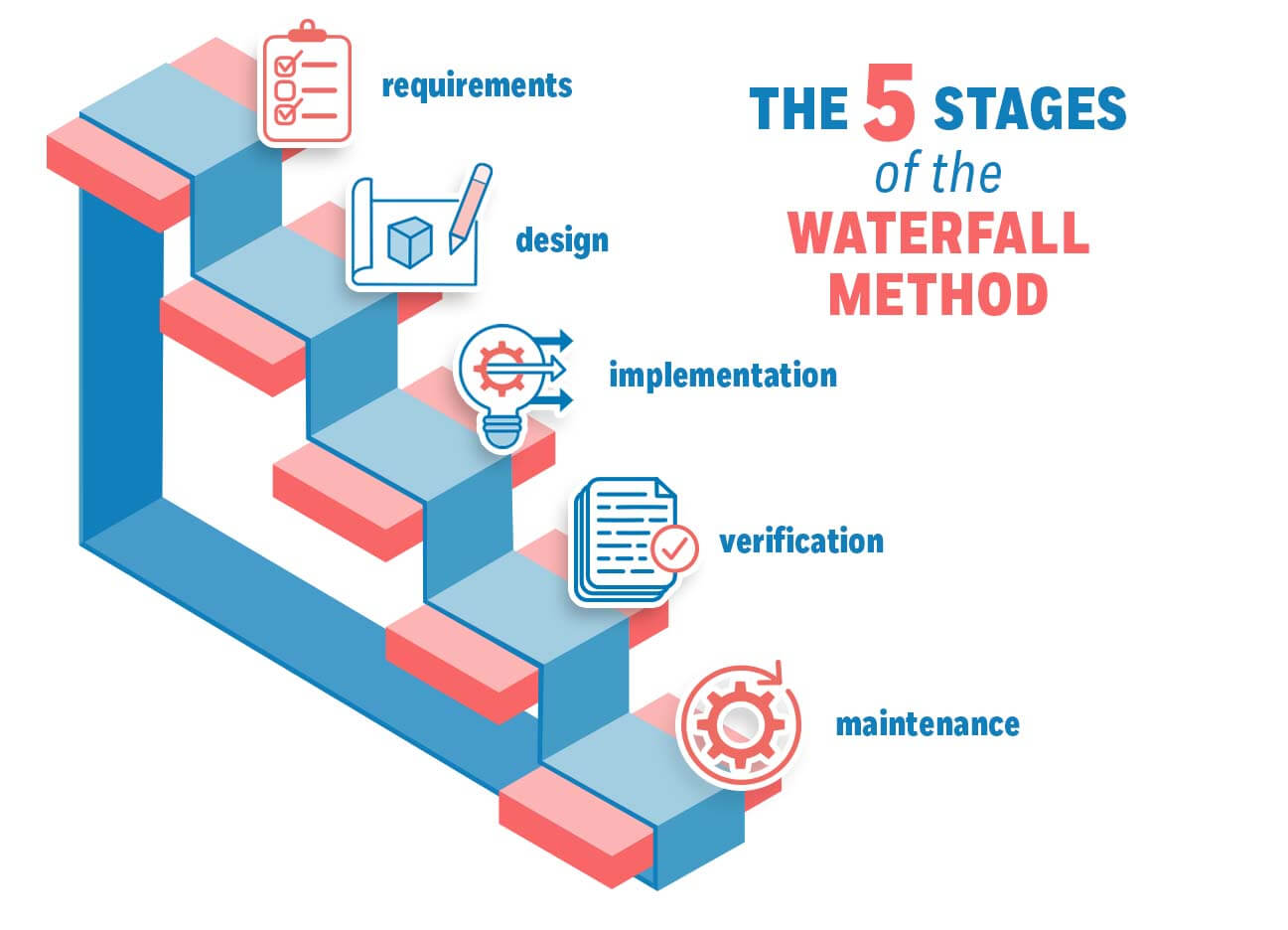
The Waterfall methodology — also known as the Waterfall model — is a sequential development process that flows like a waterfall through all phases of a project (analysis, design, development, and testing, for example), with each phase completely wrapping up before the next phase begins.
The success of the Waterfall method depends on the amount and quality of the work done on the front end, documenting everything in advance, including the user interface, user stories, and all the features’ variations and outcomes.
With the majority of the research done upfront, estimates of the time needed for each requirement are more accurate, and this can provide a more predictable release date. With a Waterfall project, if parameters change along the way, it’s harder to change course than it is with Agile methodology.
Back to index of Methodologies
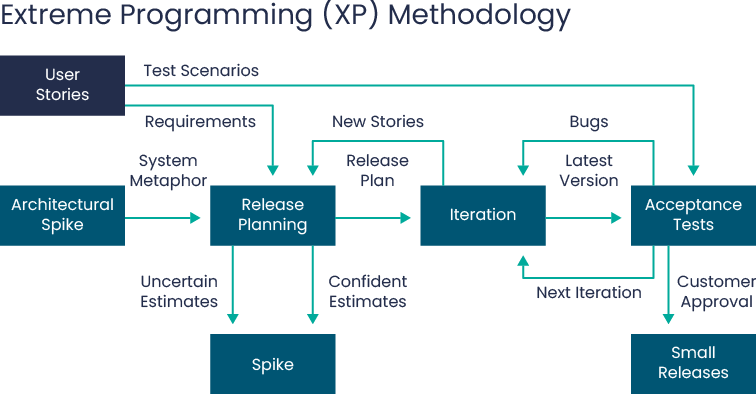
Extreme Programming, also known as XP, is useful for projects that are designed to be dynamic to changing demands. This methodology has alot of felxbility because there is constant feedback and communication between the customer and the team in order to create the
- Communication
- Simplicity
- Feedback
- Courage
- Respect
Everyone on the team works closely togther at every stage of the project.
Developers strive for simple code in order to bring more value to the product as it saves time and effort in development.
Developers deliver the software frequently and use feedback to improve the product according to the requirements.
Programmers objectively evaluate their own results without making excuses and are always ready to respond to changes.
Every person on the team understands their efforts contribute to the common goal.
- Incremental changes
- Embracing change
- Assumed Simplicity
- Quality work
- Rapid Feedback
Small changes are made to the design a little at a time and incoporated into the plan.
Programmers support the changes the client requests for and develops a plan on how to implement the new requirements
Develvopers focus on the task important for the moment and develop the program function(s) specific for the task.
A team that works well creates a valuable product and instills pride in the program
Team members accept feedback and promptly conduct the appropriate changes to the program.
Back to index of Methodologies
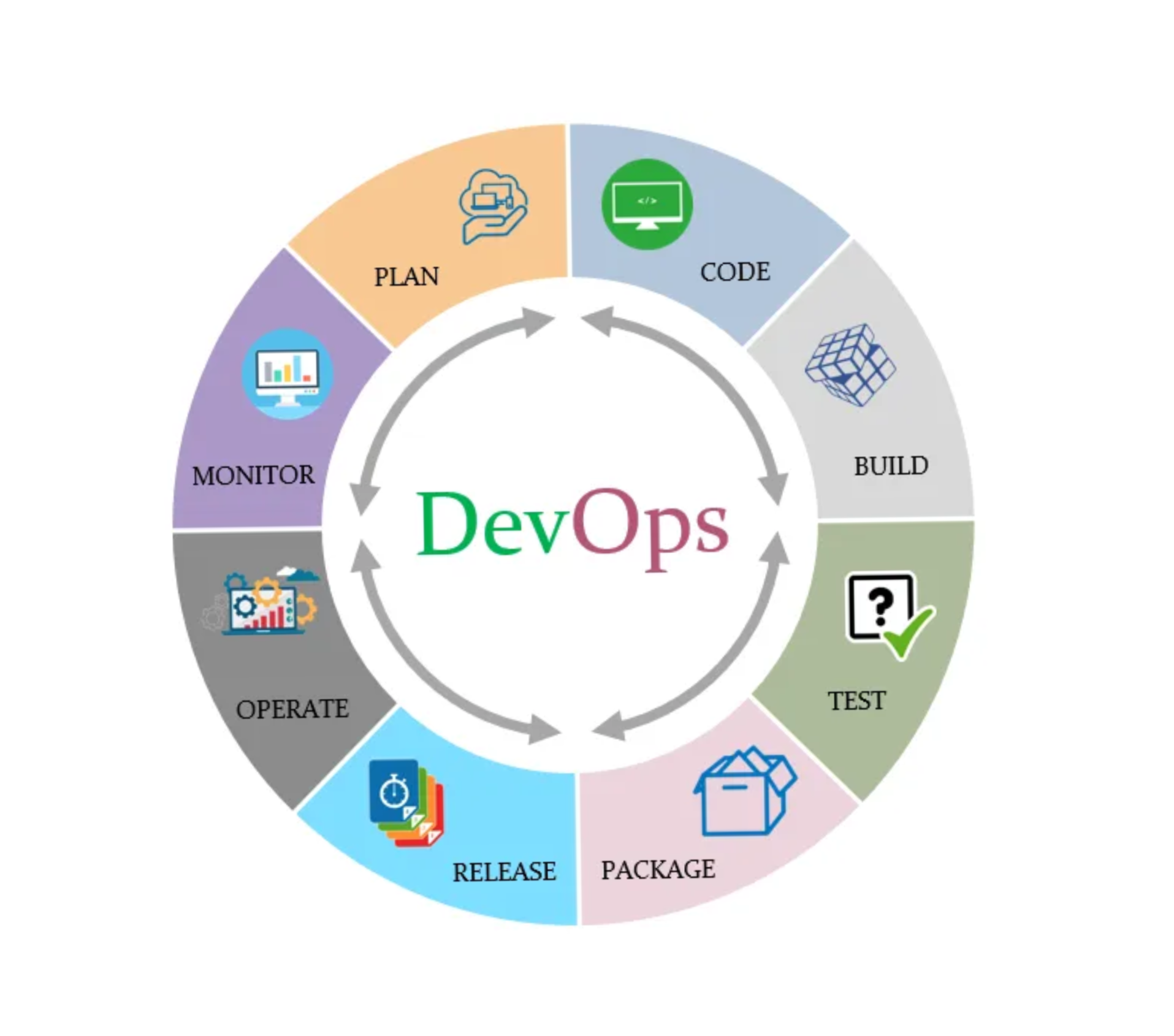
DevOps is a software development methodology that combines the development and information technology operation teams together during the entire service lifecycle - from development process to production support.
- Continuous Integration
- Continuous Delivery
- Microservices
- Infrasture as Code
- Monitoring and Logging
- Communication and Collaboration
Back to index of Methodologies
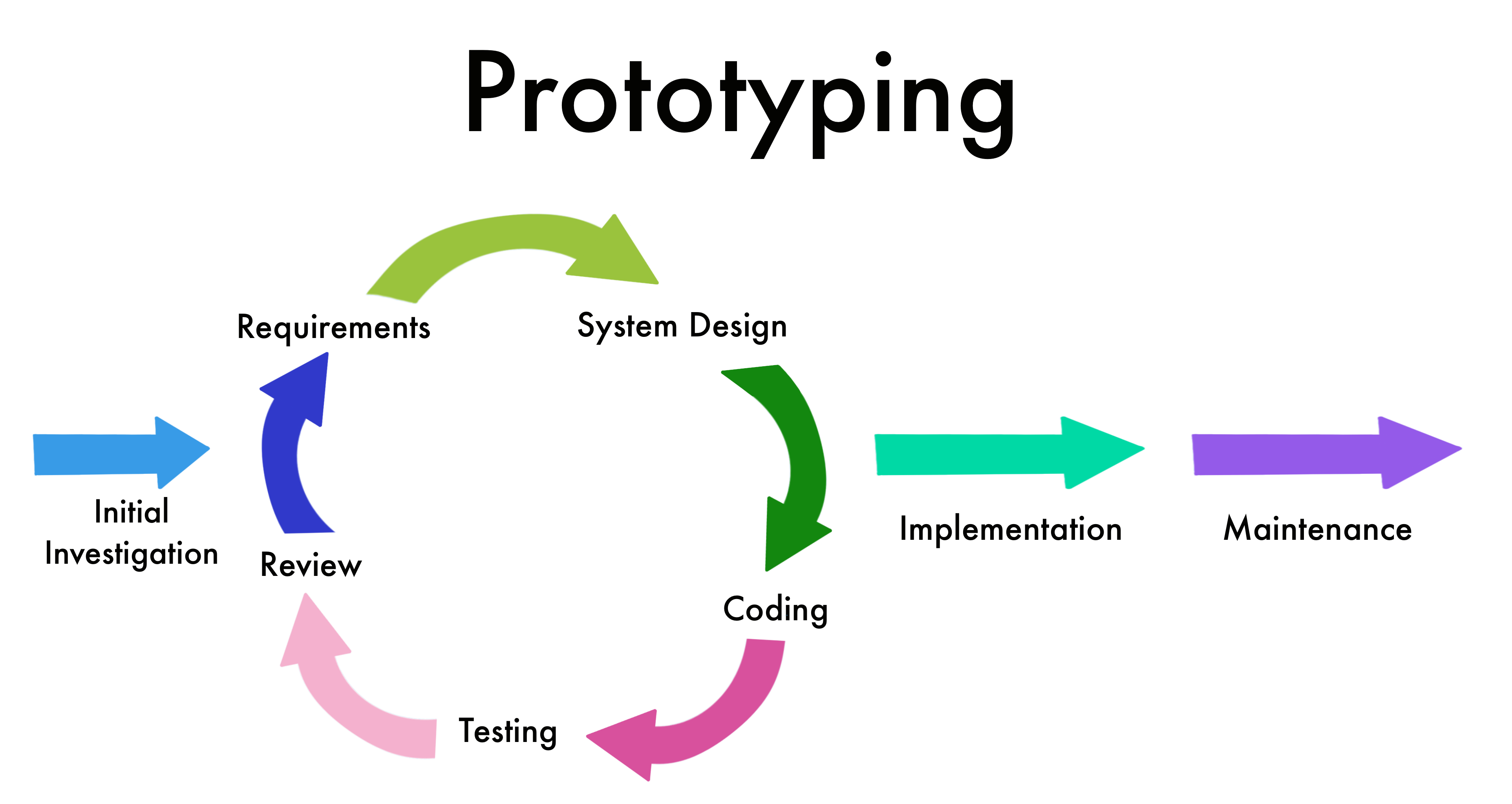
The prototyping model is a system's development method thats works best if all the project requirements are not known in detail ahead of time. Therefore, an end product is developed, tested, and refined according to the customers feedback till an acceptable prototype is achieved. The process is a trial-and-error process that takes place between the developers and the users.
- Rapid throwaway
- Evolutionary
- Incremental
- Extreme
This method involves exploring ideas by quickly developing a prototype based on preliminary requirements that is then revised through customer feedback. The name rapid throwaway refers to the fact that each prototype is completely discarded and may not be a part of the final product.
This approach uses a continuous, working prototype that is refined after each iteration of customer feedback. This method saves time and effort because each prototype is not started from scratch.
This technique breaks the concept for the final product into smaller pieces and prototypes are created for each one. In the end, these prototypes are merged into the final product.
This prototype model is used specifically for web development. All web prototypes are built in an HTML format with a services layer and are then integrated into the final product.
Back to index of Methodologies
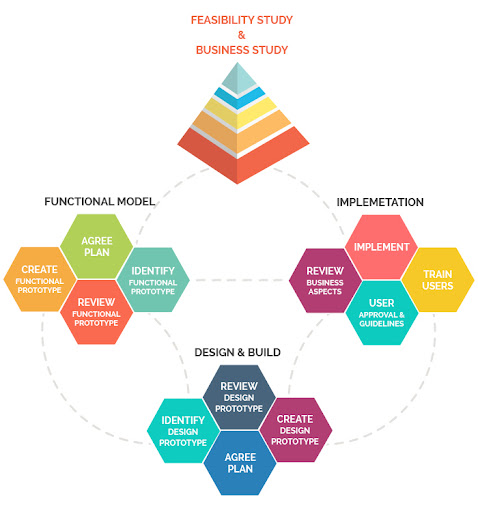
The Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM), a framework that seeks to enhance an overall process through team improvement.
- Focus on the business need
- Deliver on time
- Collaborate
- Never compromise quality
- Build incrementally from firm foundations
- Develop iteratively
- Communicate continuously and clearly
- Demonstrate control
Back to index of Methodologies
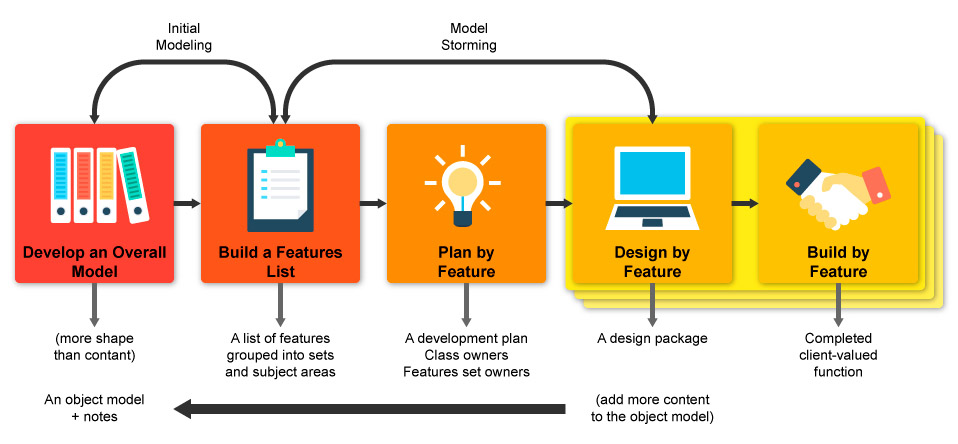
Feature-driven development (FDD) is a development methodology that emphasizes the delivery of small, incremental features or units of functionality as the primary means of progress.
Each feature is developed through a series of small, well-defined steps, called "development cycles," which involve a series of activities such as planning, designing, building, and testing. These development cycles are typically focused on the delivery of a single feature at a time, which allows the development team to focus on a small, well-defined scope of work and to deliver working software to the customer as quickly as possible
Feature Driven Develpment (FDD) is an agile approach that is designed to be flexible and responsive to changing requirements and priorities.
- Develop overall model
- Build feature list
- Plan by feature
- Design by feature
- Build by feature
Back to index of Methodologies
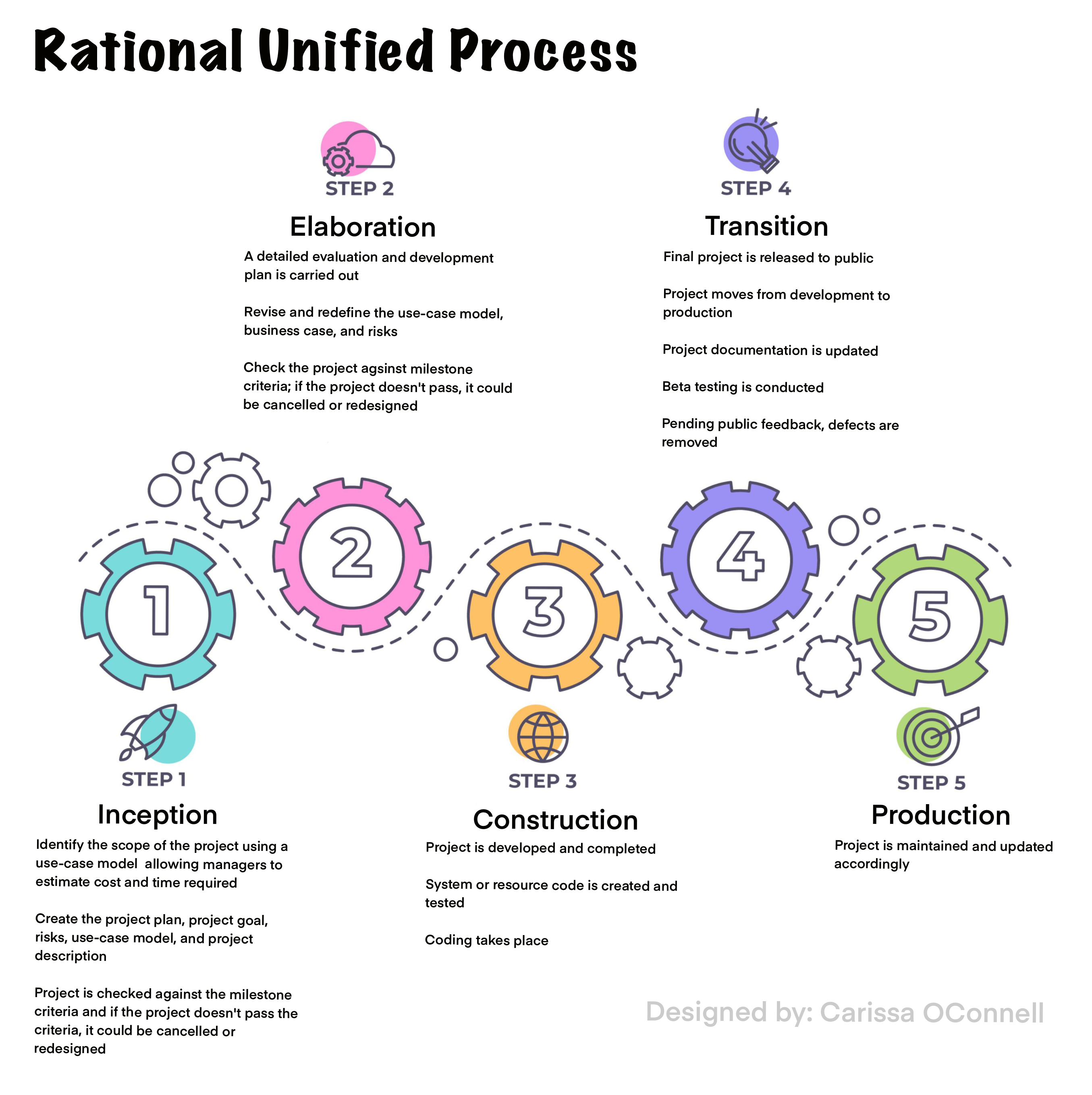
Rational Unified Process (RUP) is a software development process for object-oriented models and is also known as the Unified Process Model. Its primary purpose is to enable the creation of high-quality software that satisfies the end user’s requirements within a predictable budget and timeframe.
- Iterative and incremental development
- Strong focus on requirements
- Architecture-centric development
- Component-based development
RUP emphasizes iterations, or cycles, of work, rather than trying to complete all work upfront. This allows for more flexibility and responsiveness to change. Each iteration results in a working version of the software that can be demonstrated to, and used by, clients.
RUP puts strong emphasis on requirements gathering and management. A project’s success depends on having a clear understanding of what the client wants the final product to do. Only then can developers and project managers plan out the necessary steps to create it.
RUP takes an architecture-centric approach, meaning that the software’s overall design is created first before any code is written. This ensures that the final product will be well-structured and maintainable.
Component-based development is a technique for building software systems from pre-existing components rather than from scratch. This speeds up development time and results in more reliable code since proven components are reused.
Back to index of Methodologies
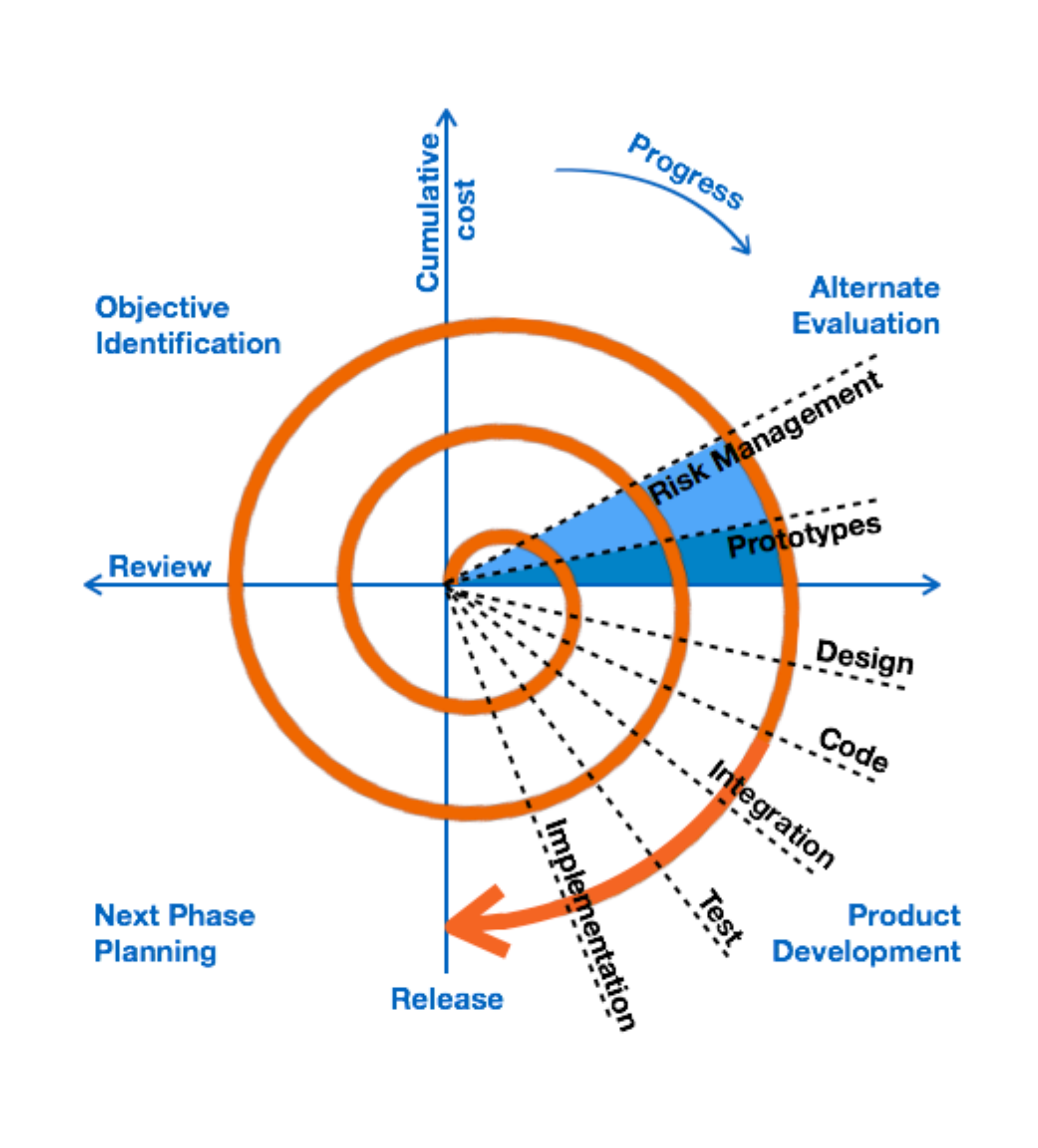
The spiral model uses a systematic and iterative appraoch to software development. Each spiral represents a phase of the software development. The number of spirals, or loops, for the project are unknown and the number of spirals varies from project to project.
- The client/customer is unsure about the requirments
- Requirements are complex and need clarity
- Significant changes are expected during the development cycle
- The project has moderate to high risk
Each iteration of the spiral represents a complete software devleopment cycle. Each cycle consists of a new planning phase based on the results of the last evaluation.
- Planning
- Risk analysis
- Engineering
- Evaluation
- Planning
Back to index of Methodologies
 Image by vectorjuiceon Freepik
Image by vectorjuiceon Freepik
Joint Appplication Development (JAD) is a process aimed at bringing the stakeholders, developers, and users together in joint sessions. A joint session is a workshop where project requirements and design are defined. The purpose of the design process is to have everyone come to a common consensus for the project requirements and to foster effective and efficient communication between all who are involved.
- Invite Relevant People
- Set Clear Goals
- Conduct Meetings Offsite
- Limit sessions
- Use Appropriate Tools
- Create Deliverables
- Final Approvals
JAD sessions ideally have 10 or fewer participants. Of those, you should always have a facilitator, key executive, end-user representative, developer, note-taker, and relevant specialists.
Each session you conduct should have clearly defined goals and outcomes. Define what you will discuss and any deliverables that will be expected.
To ensure meeting participants can focus and are not pulled away for other tasks, conduct meetings outside of the workplace.
You should hold no more than 10 JAD sessions or workshops to ensure the project gets defined in a reasonable time period.
During sessions you will want to make certain members have access to the necessary tools, which can include project management software, prototyping tools, and flowcharts.
At the end of your sessions, the facilitator should walk away with a clear project definition, system prototypes, user-interface designs, timeframe estimates, budget and resource needs, and any database schema the program will require.
YAt the end of your JAD sessions you will need to obtain approval from the key executive, as well as the end-user representative.
Back to index of Methodologies
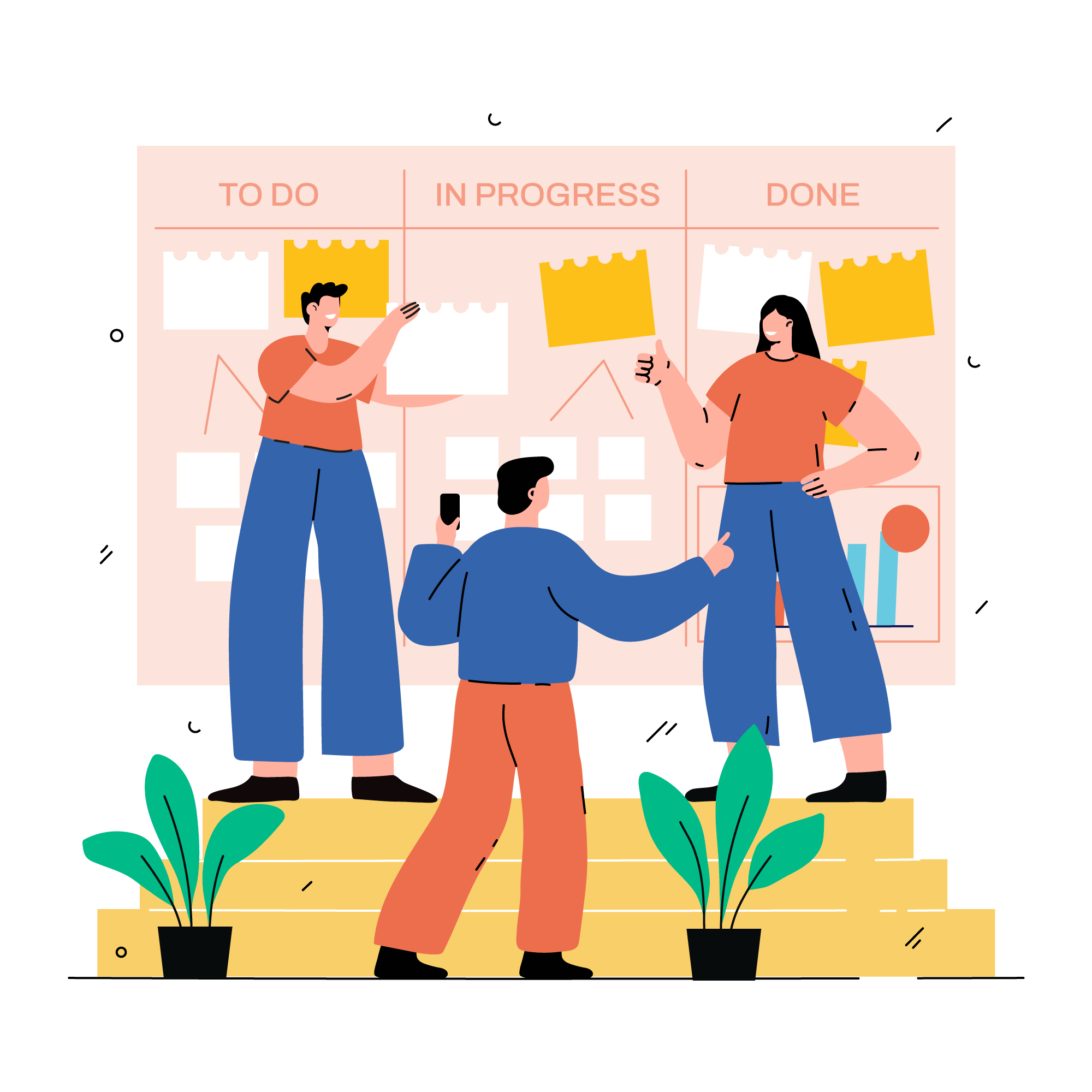

Kanban methodology is a visual way that allows the team to visualize the project development process by using kanban boards and kanban cards.
- Start with what you’re doing now
- The first step when implementing kanban is to focus on what the organization is currently doing. Don’t make changes to your process immediately, but use kanban to visualize your current workflow and begin making improvements.
- Changes occur organically over time and shouldn’t be rushed
- One of the key aspects of kanban is the notion of continuous improvement, which consists of making small, incremental changes based on careful observation of workflows instead of making radical changes.
- Respect current roles and responsibilities
- Implementing the kanban methodology doesn’t require any change in the organizational structure of teams. Changes in roles and responsibilities might come as the continuous improvement process advances but aren’t part of the kanban methodology.
- Encourage leadership from everyone
- Kanban promotes a collaborative atmosphere where team members can suggest improvement opportunities to help keep the mandate of continuous improvement for maximizing efficiency.
- Visualize workflow, whether through a physical board or kanban software
- The Kanban board features three stages:
- To-do
- In progress
- Completed
- Limit work-in-progress to keep teams executing tasks quickly
- At any point in time, the Kanban board has just the right amount of work cards that can be handled by the resources available
- Manage and improve workflow by observing work and resolving bottlenecks
- Flow refers to the movement of work items across stages of a process. The project manager keeps the workflow moving quickly while keeping an eye on blocks, bottlenecks, and risks
- Be explicit with process policies: define and share them
- Have feedback loops, such as review stages, to deliver the end product to the customer as quickly as possible
- By having an explicit understanding of issues, operations, and rules, discussions become more rational and objective
- Improve collaboratively, evolove experimentally
- By using a model to predict the effect of change, it allows the team to have a shared comprehension of problems
- Some of the models include:
- The Theory of Constraints
- The Theory of Profound Knowledge
- The Lean Economic Model
Back to index of Methodologies
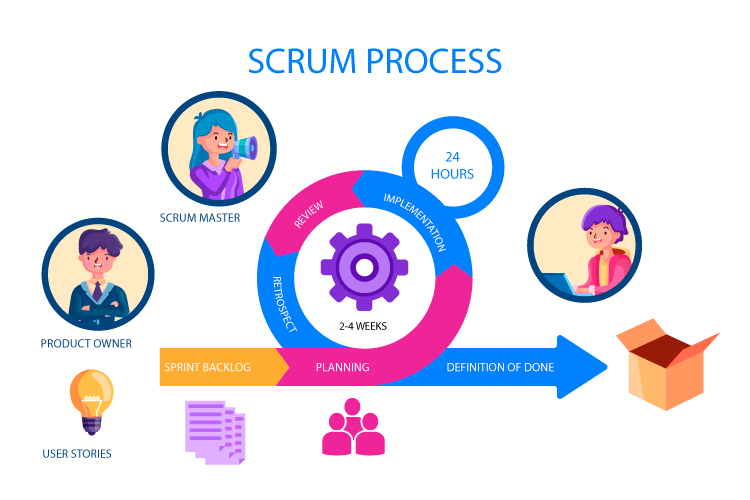
Scrum is a methodology that works in short cycles, called sprints, which has ongoing feedback. During a sprint, an inspection and adaption of the process occurs of what is expected to be delivered. Scrum is an empirical process, where decisions are based on observation, experience and experimentation. Scrum has three pillars: transparency, inspection and adaptation. This supports the concept of working iteratively.
- Courage
- Each member has the courage to do the right thing and work on tough problems
- Focus
- Everyone fosuces on the work of the Sprint and the goals of the Scrum Team
- Commitment
- Everyone personally commits to achieving the goals of the Scrum Team
- Respect
- Scrum Team members respect each other to be capable, independent people
- Openness
- The Scrum Team and its stakeholders agree to be open about all the work and the challenges with performing the work
Back to index of Methodologies
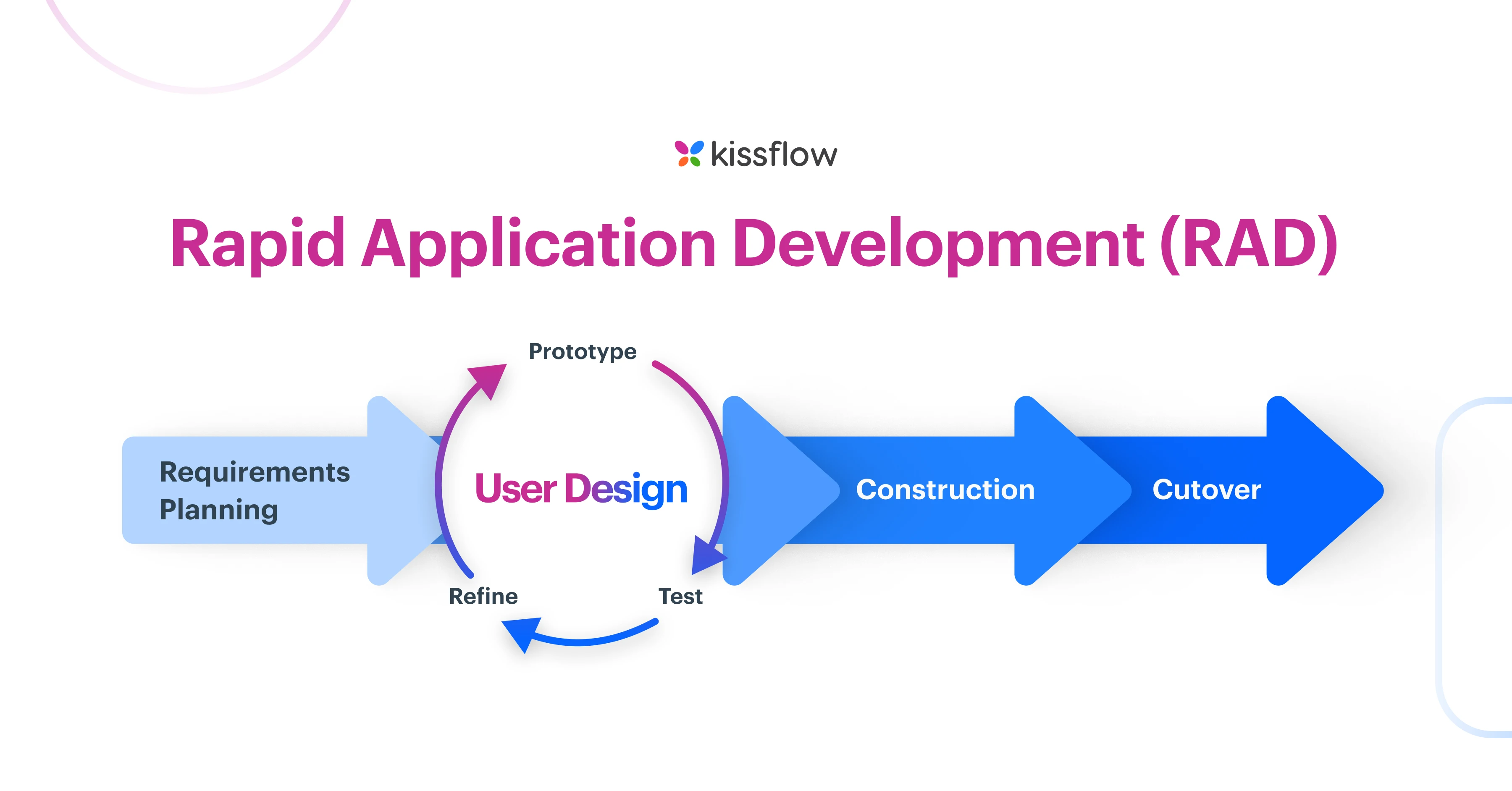 Image credit: Kissflow
Image credit: Kissflow
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is an adaptive software development model based on prototyping and quick feedback. It prioritizes development and building a prototype rather than planning. With RAD, developers are able to quickly make iterations and updates to the software without starting from scratch and the final outcome is mostly likely closely aligned with the end users' requirements.
- Define the requirements
- Prototype
- Construct
- Deploy
Back to index of Methodologies
 Image by vectorjuiceon Freepik
Image by vectorjuiceon Freepik
updates are made continuously, piece-by-piece, enabling software code to be delivered to customers as soon as it is completed and tested.
- Continuous integration
- Changes from different developers are merged back to main branch as soon as possible and then validated through automated tests to avoid integration-related issues
- Continuous delivery
- Continuous delivery automatically implements all verified code and pushes it from the build stage into testing and/or production environments. It employs an automated release process
- Continuous deployment
- Continuous deployment skips all of that and pushes every test-validated update live, into the hands of the end user
- Continuous testing
- Automated, ongoing testing helps ensure that the changes moving forward are effective and of sufficient quality
